Memory
Have you ever been people watching and notice how individuals act very differently within a particular space or moment? An extreme example could be how one acts at a Cubs game versus a networking event. Experiences and place can, and should create a strong microculture with its own set of socially agreed upon interactions. These interactions create more memorable places and allow you to interact with others and share your experiences.
Supporting Documents: Connection to Memory
Mindset: The New Psychology of Success
By Carol S. Dweck
"Carol S. Dweck, Ph.D., discovered a simple but groundbreaking idea: the power of mindset. In this brilliant book, she shows how success in school, work, sports, the arts, and almost every area of human endeavor can be dramatically influenced by how we think about our talents and abilities. People with a fixed mindset—those who believe that abilities are fixed—are less likely to flourish than those with a growth mindset—those who believe that abilities can be developed. Mindset reveals how great parents, teachers, managers, and athletes can put this idea to use to foster outstanding accomplishment."
Article Link Here
My Life with Bob
By Pamela Paul
"Imagine keeping a record of every book you've ever read. What would this reading trajectory say about you? With passion, humor, and insight, the editor of The New York Times Book Review shares the stories that have shaped her life."
Article Link Here
Binge Reading Disorder
By: Nikkitha Bakshani
"The typical American consumes more than 100,000 words a day and remembers none of them."
"People are more likely to tweet a link to an article if they have not read it fully."\
Article Link Here
Why We Forget Most of the Books We Read
By: Julie Beck
"Pamela Paul’s memories of reading are less about words and more about the experience. “I almost always remember where I was and I remember the book itself. I remember the physical object,” says Paul, the editor of The New York Times Book Review, who reads, it is fair to say, a lot of books. “I remember the edition; I remember the cover; I usually remember where I bought it, or who gave it to me. What I don’t remember—and it’s terrible—is everything else.”"
Article Link Here
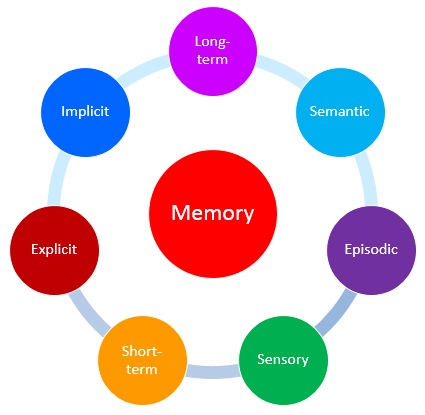
Classification of Memory
By: The Peak Performance Center
"Memory is the mental function that enables you to acquire, retain, and recall sensations, impressions, information, and thoughts you have experienced.
There are several different types, stages, classifications, and functions of memory. Most people think of memory as either short-term or long-term. However, memory can be divided into many more types or categories. We categorize short-term and long-term as stages of memory than types of memory. Types of memory are mostly subsets of long-term memory."
Article Link Here
Why Do We Remember Certain Things, But Forget Others?
By: Shahram Heshmat
"A normal function of emotion is to enhance memory in order to improve recall of experiences that have importance or relevance for our survival. Emotion acts like a highlighter pen that emphasizes certain aspects of experiences to make them more memorable. Memory formation involves registering information (encoding), processing and storage, and retrieval."
Article Link Here
Eight Ways to Remember Anything
By: Alex Lickerman
"I once came up with a metaphor I thought perfectly captured the sheer mass of material my classmates and I were expected to memorize in our first two years of medical school: it was like being asked to enter a grocery store and memorize the names of every product in the store; their number and location; and every ingredient in every product, in the order in which they appear on the label—and then to do the same thing in every grocery store in the city."
Article Link Here
Episodic Memories and Your Experiences
By: Kendra Cherry
"Episodic memory is a category of long-term memory that involves the recollection of specific events, situations, and experiences. Your memories of your first day of school, your first kiss, attending a friend's birthday party and your brother's graduation are all examples of episodic memories. In addition to your overall recall of the event itself, it also involves your memory of the location and time that the event occurred.
Closely related to this is what researchers refer to as an autobiographical memory or your memories of your own personal life history. As you can imagine, episodic and autobiographical memories play an important role in your self-identity."
Article Link Here
Research Homepage
Future of... The Future / Experience Design
Attributes
Experience Card | Narrative / Social Dynamic / Sensory Engagement / Spatial
Case Studies
Adler Planetarium / Birch Aquarium / California Academy of Sciences / De Young Museum / Exploratorium / Museum of Science and Industry / NeoCon 2018 / Salk Institute / San Francisco Museum of Modern Art / The Shedd Aquarium / The Tech Museum of Innovation / Torrey Pines Gliderport / Under Armour Brand House / The Wave Organ / VDTA Experience Survey